China’s “blue territory” and the technosphere
Posted: April 19, 2017 Filed under: Academic debates, South China Sea | Tags: academia, blue territory, Chinese nationalism, Haus der Kulturen der Welt, HKW, maritime disputes, PRC maritime law enforcement, south china sea, technosphere, UNCLOS, UNCLOS and South China Sea 1 CommentI recently contributed an essay to Technosphere, a multimedia online magazine based out of Berlin’s Haus der Kulturen der Welt (HKW): China’s “Blue Territory” and the Technosphere in Maritime East Asia.
According to the magazine’s calculations, it’s a 648-second read.
It’s part of a set of presentations that comprise a dossier on the theme of land and sea. I can recommend checking out some of Technosphere’s other dossiers, especially those on creolized technologies and risk and resilience.
My contribution contains some of the arguments developed in my PhD thesis, which fortunately is now done and dusted. It’s titled “Chinese Popular Nationalism and PRC Foreign Policy in the South China Sea” — as always comments and criticisms are much appreciated, so if you feel like taking a look, you can download it by clicking on the title.
Comparison of Vietnam and China’s joint statements, 2011-2017
Posted: February 3, 2017 Filed under: China-Vietnam, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, South China Sea | Tags: arbitration, China-Vietnam, China-Vietnam joint statement, China-Vietnam relations, joint communique, Nguyen Phu Trong, nine dashed line, nine-dash line, Philippines vs China arbitration, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, South China Sea arbitration, UNCLOS, UNCLOS and South China Sea, Vietnam-China joint statement 2 Comments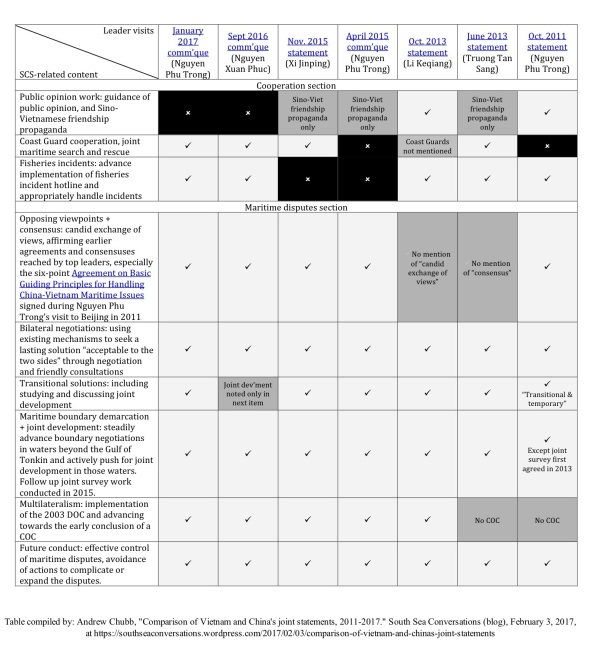
Comparison of Sino-Vietnamese joint statements since 2011 (click to enlarge). Links to sources: January 2017 communique (Nguyen Phu Trong visit to China); Sept 2016 communique (Nguyen Xuan Phuc visit to China); Nov. 2015 statement (Xi Jinping visit to Vietnam); April 2015 communique (Nguyen Phu Trong visit to China); Oct. 2013 statement (Li Keqiang visit to Vietnam); June 2013 statement (Truong Tan Sang visit to China); Oct. 2011 statement (Nguyen Phu Trong visit to China).
East Asia Forum has kindly published a piece from me on recent developments in Sino-Vietnamese relations. To supplement it, i’m posting here a table comparing the South China Sea-related elements of the last 7 joint statements between the two.
The comparative table was the basis for the article’s argument that General Secretary Nguyen Phu Trong’s visit to Beijing last month did not involve any softening of Vietnam’s position on the issue.
According to a knowledgeable Vietnamese source, there are three types of Sino-Vietnamese bilateral joint statements issued after high-level meetings. In ascending order of importance these are:
- Joint press release (联合新闻公报, thông cáo báo chí)
- Joint communique (联合公报, thông cáo chung)
- Joint statement (联合声明, tuyên bố chung)
These documents are often not released in English, and some of the translations that have appeared have been incomplete or unreliable, so the table above compares the Chinese full text as published by state media (links are in the caption area above).
The table also includes an item, not discussed in the EAF article for space reasons, on cooperation in public opinion work. In the 2011 joint statement, the two sides pledged cooperation on “strengthening public opinion guidance and management” – which, in the context of several weeks of anti-China protests through the middle of that year, was tantamount to a Vietnamese undertaking to dampen anti-China sentiments.
Interestingly, however, there has been no analogous item in the recent joint documents — even after another, even more intense, wave of anti-China sentiments burst forth in 2014 during the HYSY-981 oil rig standoff. Its omission from subsequent documents might indicate an acceptance on China’s behalf of the strength Vietnamese nationalist sentiments that flow in its direction at times of heightened tensions. Perhaps also an acknowledgement that Hanoi is already doing what it can to promote Sino-Vietnamese friendship? Any other readings?
The EAF piece is reposted below. Based on some early feedback, i should have been clearer that in suggesting . . .
China may have pulled back from its pursuit of particular claims that have no basis in international law
. . . i do not mean the PRC has seen the light and is abandoning all claims deemed unlawful in the UNCLOS arbitration. Just that there are some unlawful aspects of China’s claims that it is no longer pushing, and this has removed some of the major drivers of Sino-Vietnamese tensions.
As always, further comments, arguments, additions and corrections are much appreciated.
South China Sea arbitration: don’t count on a decisive Philippines win
Posted: July 10, 2016 Filed under: China-Philippines, State media, Xinhua | Tags: AIIA, arbitration, Australian Institute of International Affairs, China-Philippines relations, external propaganda, Law of the Sea, Philippines vs China arbitration, Philippines vs China case, south china sea, South China Sea arbitration, UNCLOS, UNCLOS and South China Sea, 强词夺理 1 Comment
Thomas A. Mensah, Presiding Arbitrator of the Philippines vs China arbitral tribunal. Among Judge Mensah’s many qualifications, he was the inaugural President of the ITLOS, on which he served from 1996 to 2005. Contrary to PRC propaganda claiming the arbitral tribunal is “presided over by a former Japanese diplomat” Judge Mensah is from Ghana.
Here’s a bit of speculation ahead of the UNCLOS arbitration decision on Tuesday, written for the Australian Institute of International Affairs’s website.
My argument is that, however shrill and legally unconvincing the PRC’s propaganda campaign may seem, it will force the tribunal to take politics into account to an even greater extent than it would have otherwise — so expect some significant concessions to China. As Bill Bishop points out, the CCP has a long tradition of overcoming deficiencies of reason via sheer force of rhetoric (强词夺理). Of course, i could be proved wrong in short order; if so, things may get very interesting for the PRC’s relationship with the UNCLOS.
I’ve also added in the page numbers of the article’s references to the tribunal’s Award on Jurisdiction. Obviously i’m not a lawyer and it’s a case where the fine-grain details are crucial, so i’d especially appreciate any corrections.
~
South China Sea arbitration: don’t count on a decisive Philippines win
AIIA Australian Outlook
July 7, 2016
By Andrew Chubb
On 12 July, an international arbitral tribunal will hand down its findings in a landmark case brought by the Philippines against China over the South China Sea issue. The decision will have far-reaching implications, not only for this contentious maritime dispute but also for international law and politics in East Asia.
United States officials have expressed concern that the decision may exacerbate tensions in the region if China responds to an adverse finding with new assertive moves in the disputed area. However, contrary to the expectations of many observers, a total victory for the Philippines is unlikely. At least some key findings will probably favour China due in part to the political interest of the tribunal in protecting the status and relevance of the law of the sea in international politics.
The case has been particularly contentious due to China’s allegation that the Philippines is “abusing” the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) processes. China’s subsequent refusal to take part in the proceedings, relentless propaganda campaign aimed at delegitimising the tribunal among domestic and international audiences, and its frenetic efforts to enlist statements of support from foreign governments, have created a backdrop that means the tribunal is unlikely to decide the case on legal merits alone.
Even if the merits of the Philippines’ claims are strong, the arbitrators will be keen to avoid appearing to make a one-sided ruling. Instead, they will seek to make at least some concessions to China in order to neutralise Beijing’s political attacks on the tribunal’s authority, minimise the political fallout, and forestall the possibility of a Chinese withdrawal from UNCLOS. The latter scenario, while highly unlikely, would be a major disaster for the cause of international law, so it is likely to be among their considerations as legal professionals.
.
The current state of play
The Philippines has asked the arbitral panel to rule on 15 specific questions concerning the South China Sea with the aim of clarifying the limits of the sea areas that China can legally claim under UNCLOS. The Philippines’ contentions can be summarised as:
- China’s claims to “historic rights” within the nine-dash line are invalid under the Convention (submissions 1 & 2)
- Scarborough Shoal is not an island, and therefore generates no entitlement to maritime rights beyond 12 nautical miles (nm), such as an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) or Continental Shelf (submission 3)
- China’s outposts in the disputed Spratly archipelago are also not islands, and therefore also generate no EEZ or Continental Shelf entitlement (submissions 4, 5, 6 & 7)
- China has conducted maritime law enforcement and economic exploitation activities in areas where it does not have any lawful claim, thereby violating the Philippines’ lawful rights under the Convention, while also violating the Convention’s safety requirements (submissions 8, 9, 10, 13 & 14)
- China’s massive island-building projects breach the Convention’s rules on artificial islands, constitute unlawful appropriation of maritime spaces, and violate the Convention’s obligations not to damage the marine environment – as do its fishing, coral and clam harvesting activities at Scarborough Shoal and in the Spratly Islands (submissions 11 & 12)
The Philippines is also asking the tribunal to order China to drop any unlawful claims and desist from any unlawful activities (submission 15).
In response, China argues that these matters are “in essence” issues of territorial sovereignty, which UNCLOS was not intended to govern, and maritime boundary demarcation on which China has invoked its right to reject compulsory dispute resolution. Beijing also argues the Philippines is legally bound by its previous “commitments” to settle its disputes with China through bilateral negotiations.
However, in October 2015, the tribunal issued its preliminary award and found that it is competent to rule on at least seven of the Philippines’ 15 claims against China. In an official statement, China expressed anger at the ruling, this time accusing both the Philippines and the arbitrators themselves of having “abused the relevant procedures”. Notably, however, it avoided any suggestion that it was rejecting the UNCLOS itself.
.
Political considerations
Numerous analysts, including many in Manila both inside and outside government, expect that when the arbitral tribunal hands down its final award, the ruling will find in favour of the Philippines.
But as Phillipines legal academic Jay Batongbacal has noted, the tribunal had a strong incentive to accept jurisdiction over the case because doing otherwise would have been tantamount to an admission that UNCLOS is irrelevant in one of the world’s most important waterways, and one of its most dangerous maritime hotspots.
However, the same considerations make a total victory for the Philippines unlikely. Not only would this outcome draw even more furious political attacks on the tribunal’s authority from China, a decision seen as one-sided would increase the rhetorical bite of Beijing’s international propaganda.
The Award on Jurisdiction issued last October foreshadowed findings favourable to China on some key issues. For example, it noted that if China’s island-building and law enforcement actions are found to be “military in nature” then it may be unable to rule on their legality as these are excluded from the Convention’s dispute resolution procedures (p.140).
Perhaps even more importantly, the Award (pp.62-63) also flagged the possibility of the tribunal providing an implied reading of the nine-dash line’s meaning for China: development that could effectively legalise the PRC’s infamously unclear and expansive claim.
.
What to expect
The case’s greatest significance may lie in providing the first legal precedent defining specific criteria for what constitutes an “island” (entitled to an Exclusive Economic Zone and Continental Shelf under UNCLOS), as opposed to a “rock” (which is only entitled to 12 nautical miles of territorial sea).
Previous international legal rulings have deliberately avoided this question, but the Philippines’ submission has put the issue front and centre. The Award explicitly noted that “the Philippines has in fact presented a dispute concerning the status of every maritime feature claimed by China” in the disputed area (p.72). This suggests the tribunal may make the long-awaited definition. This would also accord with the arbitrators’ imperative to maximise UNCLOS’ relevance in international politics as it would help clarify the status of other disputed maritime rights claims in Asia and beyond, notably Japan’s claim to a 200nm EEZ around Okinotorishima.
It is no certainty that this will happen. It remains possible that the tribunal would simply rule that there may exist one or more islands within 200nm of the relevant areas: a conclusion that would be sufficient to prevent consideration of the Philippines’ claims against China in those areas.
Although the case is too complex to predict specific findings with certainty, the Philippines’ best hopes probably lie in obtaining an explicit rejection of China’s claims to “historic rights” and an affirmation that Scarborough Shoal—but not the much larger Spratly archipelago—is a rock and not an island, meaning the surrounding waters outside 12nm cannot be subject to any legitimate Chinese claim.
US officials worry that the ruling may exacerbate tensions in the region if China responds to an adverse finding with more assertive moves. Reclamation activities at Scarborough Shoal and the declaration of an Air Defense Identification Zone in the South China Sea have been touted as possible responses.
Despite China’s decision to ignore the tribunal’s verdict, it has major stakes in UNCLOS’ ongoing viability. These include deep seabed mining concessions in international waters and its outer continental shelf claim in the East China Sea. UNCLOS is also central to China’s argument that US naval surveillance activities off its coast are illegal.
This leaves Beijing in the awkward position of trying to cast itself as a defender of UNCLOS while ceaselessly attacking an arbitration process constituted directly under its auspices. The continuation or even intensification of China’s political campaign threatens the global authority of UNCLOS as it seeks to divide signatory states into opposing camps. I may be proved wrong on Tuesday but I suspect the SCS tribunal’s arbitrators will be only too aware of this as they prepare their ruling.
“The arbitrators will themselves be judged by history”: domestic aspects of China’s UNCLOS propaganda blitz
Posted: June 27, 2016 Filed under: Article summaries, China-Philippines, Mouthpieces, People's Daily, South China Sea, State media, Xinhua | Tags: arbitration, contradictions, dialectics, external propaganda, People's Daily, Renmin Ribao, south china sea, South China Sea arbitration, UNCLOS, Zhong Sheng 2 Comments There has rightly been plenty of attention directed towards the PRC’s furious campaign to enlist, or at least appear to enlist, international support for its rejection of the arbitral tribunal that will shortly adjudicate on 15 complaints about China’s actions in the South China Sea. The latest broadside against the tribunal from the People’s Daily is a helpful reminder of some domestic aspects shaping the propaganda blitz.The wave of propaganda from China’s English-language mouthpieces (and presumably those in other languages too) is certainly not receding, and in fact judging by Xinhua’s Twitter stream it is gathering momentum.
The weekend just gone brought forth one of the more brazen pieces of propaganda from Xinhua, titled, Turkey agrees China’s stance for resolving disputes via dialogue. Readers who clicked through to the story may or may not have noticed that by “Turkey,” the article was in fact referring to Dogu Perincek, Chairman of the Patriotic Party, which has zero seats in the Turkish parliament, and who just recently got out of jail following one of Erdogan’s crackdowns.
But “Chairman of the Turkish Patriotic Party” sounds quite legitimate and credible, at least when translated into Chinese. Not surprisingly, then, the story was widely publicized in the domestic media under the headline: Turkish Patriotic Party Chairman says China has no duty to obey the South China Sea arbitration ruling.
This points to the importance of domestic considerations shaping China’s campaign to delegitimize the UNCLOS arbitration. As is so often the case, domestic may help explain quite a bit: the curiously un-legalistic tone of China’s critiques of the international legal process, with lots of high-strung rhetoric of brazen betrayals and malicious conspiracies instead; a fixation with getting foreigners to back the PRC’s position (even as the Beijing maintains its resolute opposition to “internationalizing” the issue); and a conga-line of usually obscure domestic organs lining up to say exactly the same thing, from the China Society of the Law of the Sea to the China Fisheries Association.
Besides pursuing the ever-elusive goal of “unified thinking” among party and military, there are good reasons why the CCP would be concerned about shoring up support among the general public in China. In early 2013, before the PRC had gone public with its rejection of the arbitration, about 6 out of 10 urban survey respondents indicated that they thought international arbitration sounded like a reasonable way of handling the South China Sea disputes. The article that appears below in summary translation, from the People’s Daily‘s foreign affairs commentary team “Zhong Sheng,” seems illustrative of how hard the CCP is trying to delegitimize the arbitration among domestic audiences. It appeared on p.3 of the official party mouthpiece, and became a top headline throughout the day on major commercial news portals on June 27.
The article also makes plain the PRC’s heavy stake in the ongoing viability of the UNCLOS system, which has put China is in the awkward position of trying not to undermine the convention while ceaselessly attacking an arbitration process constituted directly under its auspices. This may seem hopelessly contradictory, but in the CCP’s eternally-correct dialectical approach to policy there’s generally a way for the party to have its cake and eat it too. In this case, the correct handling of the contradiction lies in convincing domestic and international audiences that China is in fact defending the authority and integrity of the UNCLOS by rejecting the arbitration. Not only is the Philippines maliciously “abusing” the process, and the US hegemon puppeteering behind the scenes, the arbitrators themselves are reckless and ill-intentioned co-conspirators who will be judged by history.
(Now just repeat ad nausem and — bingo! — another contradiction inevitably resolved…as long as the immutable laws of history haven’t been infiltrated by those same shadowy forces who got to the law of the sea.)
Appearing next to the article in the People’s Daily print version was a piece proclaiming that participants at a conference at Leiden University, co-organized with Wuhan University, had concluded: Philippines’ South China Sea arbitration violates international legal principles. An English version of the latter piece is available here: Int’l experts question proceedings of South China Sea arbitration.
~
Zhong Sheng: China’s inevitable choice of determination and capability
中国意志和能力的必然选择(钟声)
2016/06/27
Top headline on Sina, QQ, Baidu, Huanqiu, NetEase news platforms under headline. “Party paper: China completely capable of towing away Philippines ship on Second Thomas Shoal”
“Zhong Sheng” begins by observing that America’s pushing of the militarization of the SCS and words and deeds showing off its weaponry, have deepened China’s concerns about harm to its own interests, and raised China’s resolve to increase its capabilities to defend those interests.
Of course, the islands of the SCS belong to China and no country even said anything to the contrary otherwise until the 1970s. But then,
“tempted by the prospect of resources, the Philippines and other countries, under the excuse that the islands were within 200nm of their shores, attempted to using maritime administrative rights claims to negate China’s sovereignty over the Spratlys. To use a common expression, China’s Spratly islands were looted.”
As to why the PRC allowed this to happen,
“it wasn’t because China did not have the ability to stop the illegal occupations, but rather because of China’s extremely restrained response. However, China has bottom lines, and no Chinese government administration has made any compromise on the sovereignty questions. Today, in the southern part of the South China Sea China does not have a single oil well, Chinese fishing boats are often impounded, and fisherfolk often detained. People should ask whether this is the ‘strong bullying the weak’ or the ‘weak bullying the strong.’ “
Since the 1960s China has settled border disputes with 12 out of 14 land neighbours. This is “the best example of China resolving disputes through bilateral negotiation, of its independent foreign policy, its peripheral diplomacy policy of good-neighbourliness, and its practice and upholding of international law.”
The story of Second Thomas Shoal, according to Zhong Sheng, is evidence of China’s good intentions:
“China is completely capable of towing away the Philippine ship grounded there, but for the sake of the overall situation of stability in the SCS, China has kindly and patiently waited, all along maintaining an extremely restrained attitude.”
The Philippines’ has openly engaged in vile treachery 背信弃义 by requesting arbitration, Zhong Sheng tells readers, for in 2011 Pres Aquino agreed to joint development and promised to resolve disputes through negotiation. But then 18 months later he wantonly filed for arbitration without even telling China beforehand.
UNCLOS article 298 provides for state parties to declare non-acceptance of dispute resolution processes, including arbitration. China did this in 2006 and nearly 30 other countries have done likewise. Thus,
“China’s non-acceptance and non-participation, much less recognition, is completely in accordance with international law including UNCLOS. It is proper and legitimate, and is an action that respects international law and safeguards the integrity and authority of the UNCLOS. If the tribunal ignores basic principles of UNCLOS, and basic common sense in international law, forcing a judgement, it will set a dangerous precedent, opening a maritime ‘Pandora’s Box’, for which the arbitrators will themselves be judged by history.”
Finally, America is militarizing the SCS in the name of opposing militarization – it’s America’s ships and aircraft making waves there, and American officials who are “issuing evil words that destroy the peace and stability of the region.”
“America’s advancing of the militarization of the SCS, and its words and deeds that show off its weaponry, have deepened China’s concerns about harm to its own interests, and raised China’s resolve to increase its capabilities to defend those interests.”
China’s capabilities and determination mean that it will not compromise. However, China has no intention of becoming a world superpower, or even a regional boss.
“America absolutely does not need to worry about a strong China challenging its global interests. Ideas about treasuring peace have been handed down through the generations in China, and the gene of peace is deeply planted in the blood of the Chinese people.”
China’s maritime Great Wall and a “new Eight-Nation Alliance”
Posted: June 15, 2016 Filed under: Global Times, South China Sea | Tags: Ashton Carter, Eight Nation Alliance, France and South China Sea, Global Times, Huanqiu Shibao, Shangri-la Dialogue, south china sea, United States in South China Sea, US and South China Sea, 八国联军 2 Comments
Troops of the Eight Nation Alliance, 1900 (with the fitting addition of Australia, then still a British colony)
In lieu of normal posts (working hard to wrap up my thesis) i’m going to try taking this blog back to where it began, sharing some of the quick summary translations i do for my own purposes. They’ll be mainly Chinese media and commentary that hasn’t been reported in English. I’ll let the pieces speak for themselves, but i’d love to hear any readers’ thoughts and analysis.
The first is an op-ed from the Huanqiu Shibao on Sunday (June 12), regarding events at the Shangri-la Dialogue. Most of the article addresses US Defense Secretary Carter’s reiteration of his “Great Wall of self-isolation” line, but it also raises the strong statements on the South China Sea issue from the French Defense Minister. The latter appears to have been the basis for the striking headline, which propelled the story to the top of the agenda over at Sina and Baidu on Sunday, and onto front pages elsewhere online.
~
Expert: many western countries want to send warships to SCS, may form new Eight-Nation Alliance
专家:西方多国欲派舰赴南海 或现新八国联军
When the Great Wall meets US aircraft carrier
当中国“长城”遇上美国“航母”
(original headline from print version)
2016/06/12
Widely reposted (under the “Eight-Nation Army” headline) – top headline on Baidu News, Sina News, front page on HQW, QQ, etc.
By Liu Zhixun, fellow of the Renmin University Chongyang Financial Research Institute.
Liu frames the story as a series of “thankyous” to Ashton Carter for using his Great Wall analogy at Shangri-la, because, first of all, the Great Wall is evidence of China’s thousands of years of purely defensive strategy.
“The reason we ought to thank Mr Carter is that he has given China the best opportunity to talk about history, to tell its story. At the same time, Mr Carter’s use of the correct analogy of the the Great Wall shows the world that everything China does in the South China Sea is merely building a Great Wall, and a Great Wall’s only function is defensive.”
Aircraft carriers are “not only the strongest weapon of attack, they are also an extension of territory” — so when US aircraft carriers meet the “Great Wall” in the South China Sea, the US’s aggressive intent is laid bare. In a line picked up as the headline in the print version, Liu likens the encounter to a scholar-official meeting a soldier in ancient China, ie. civilization and reasonableness against brute force (秀才遇见兵,有理说不清). “US aircraft carriers cruising the South China Sea are clearly not there to take in the view, but to show off and cause trouble, to give a demonstration of America’s military power.”
The Great Wall also, according to Liu, shows the unconquerability of the Chinese nation (民族). “Because, a nation that can construct a 10,000-li wall is a nation that can overcome 1,000 difficulties and 10,000 dangers, a nation that no force can conquer.”
However, contrary to what Carter said, the Great Wall was absolutely not a building of self-isolation and “defense is absolutely not a synonym for isolation.” To prove this, Liu offers Carter and his Huanqiu readers a lesson in European history:
“Whether in Germany, Rome, or any number of northern European countries, you can everywhere find principalities and city states that flourished whilst protected by city walls. There is no historian or military expert in the world who could describe these cities as ‘self-isolated’. On the contrary, people give the historical function and cultural contributions of these buildings high appraisals and respect.”
“…In passing through these ancient city walls, history becomes closer and more friendly. Because they became the best textbook linking together nations with different histories, cultures and beliefs.”
Liu says China should also thank Carter for showing its young people the US’s true “bandit logic” and “hoodlum behaviour”, thereby disabusing them of any unhelpful admiration they might have had for America.
“Mr Carter has greatly helped China’s media, or China’s propaganda organs: making China’s young people treasure the importance of national unity and the urgency of state power.”
Liu concludes by stating that other western countries have been “talking nonsense 妄言” about sending ships to the South China Sea.
“Some experts have made preliminary calculations that a new “Eight-Nation Alliance” may emerge in the South China Sea. If this situation really does appear, it will carry enormous warning to the world and China: people will not forget the great powers’ invasions of China in the 19th century, and the harm they caused China. If this history is repeated, Carter will be remembered in history as an inglorious character.
“China’s Great Wall is impassable, indestructible, indispensable defensive bottom line, and no one in the world should underestimate or overlook the strength and power of China’s Great Wall.”
But Liu finishes by noting that there is “reason to believe” China and America have the ability to prevent the occurrence of a destructive conflict.
China’s latest oil rig move: not a crisis, and maybe an opportunity?
Posted: June 27, 2015 Filed under: China-Vietnam, South China Sea, Western media | Tags: China-Vietnam, China-Vietnam relations, Chinese foreign policy, HYSY-981, Nam Con Son, Nam Con Son Basin, nine dashed line, oil and gas, south china sea, straight baselines 1 Comment
Location of Chinese drilling rig HYSY-981, with approximate equidistant lines between Hainan, the Vietnamese coast, and the disputed Paracel Islands (map by Greg Poling)
On June 25, China’s Maritime Safety Administration announced the gargantuan drilling rig HYSY-981 had returned to the South China Sea for more drilling operations, raising concerns of a return of the serious on-water clashes last year.
Here we go again was a widespread sentiment on Twitter. The apparent expectations of impending repeat showdown appear to result in part from the headline of a widely-shared Reuters story, ‘China moves controversial oil rig back towards Vietnam coast‘. This might be technically correct (i’m not sure exactly where the rig was before) but this year’s situation is quite different to last year’s.
Serious on-water confrontation is unlikely this time around because the rig is positioned in a much less controversial area. It is a similar distance from the Vietnamese coast (~110nm) but much further from the disputed Paracel Islands (~85nm), and much closer to the undisputed Chinese territory of Hainan (~70nm, compared to more than 185nm in 2014).
As explained below, the parallels between this area and others where China has objected — sometimes by coercive means — to Vietnamese oil and gas activities, make the latest move a good opportunity to grasp an important aspect of the PRC’s position in these disputes, and pin down some of its inconsistencies.
Luconia Breakers: China’s new “southernmost territory” in the South China Sea?
Posted: June 16, 2015 Filed under: China-ASEAN, China-Malaysia, CMS (China Maritime Surveillance), South China Sea, State media | Tags: ASEAN and South China Sea, 《中国国家地理》, China Coast Guard, China Coastguard, China-ASEAN, China-Malaysia relations, Chinese foreign policy, Chinese National Geography magazine, 琼台礁, 马宏杰, Gugusan Beting Patinggi Ali, Hempasan Bantin, James Shoal, Luconia Shoal, Luconia Shoals, Ma Hongjie, Malaysia, Malaysia and South china SEa, normalized patrols, North Luconia Shoal, PRC foreign policy, PRC maritime law enforcement, Shahidan Kassim, Shan Zhiqiang, south china sea, South Luconia Shoal, Spratly, spratly islands, Wu Lixin, 单之蔷, 吴立新, 曾母暗沙 13 Comments
The “island” at Luconia Breakers 琼台礁/Hempasan Bantin (source: Chinese National Geography, October 2010)
In a vivid illustration of how dynamic the status quo in the South China Sea can be, an apparently new Spratly island, formed by the forces of nature, has become a source of tension between China and Malaysia.
Luconia Breakers (Hempasan Bantin / 琼台礁) is just over 100km north of James Shoal, the shallow patch of ocean that Chinese people are routinely taught is the southernmost point of their country’s “territory“, despite it being several metres underwater.
As this post will show, unlike James Shoal, the territory at Luconia Breakers actually exists above the waterline. This is significant because if the PRC ever needs to clarify the nature of its maritime claims under international law, it could end up adopting the “new” feature as its southernmost territory.
Topping off the intrigue, the train of events leading to the current Sino-Malaysian standoff may well have been set in motion by an adventurous Chinese magazine team.
Defining the “status quo” in the South China Sea
Posted: June 14, 2015 Filed under: Academic debates, China-ASEAN, China-Australia, China-Malaysia, China-Philippines, China-US, China-Vietnam, South China Sea | Tags: artificial islands, ASEAN, ASEAN and South China Sea, Ashton Carter, china maritime dispute, China-US relations, coercion, diplomacy, international norms, Malaysia, Malaysia and South china SEa, maritime disputes, reclamation, regional united front, Shangri-la Diaologue, south china sea, Spratly, spratly islands, status quo, The Diplomat, United States in South China Sea, 南海现状 9 CommentsBelow is a piece published at The Diplomat, running through what the “status quo” is in the South China Sea, and the difficulties encountered in trying to define it. Aside from identifying some key metrics of the current situation in the disputed area, the aim was generate some debate, or at least second thoughts, about the usefulness of the “status quo” as a normative standard. The concept has proved useful in diplomacy over Taiwan, Korea and elsewhere, and (arguably) in international relations theory. But given the complex, watery nature of the South China Sea dispute, i argue it’s not likely to help in establishing the kind of clear-cut, universally recognized standards the region needs to forestall escalation there.
~
The South China Sea: Defining the ‘Status Quo’
The term’s broad-brush vagueness – it simply means “the existing situation” – may make it appealing for practitioners of diplomacy, but the lack of clarity limits its usefulness as an analytic tool. More troublingly, being such an all-encompassing term, its use as a normative standard is inevitably selective, resulting in inconsistencies that risk breeding misunderstanding and mistrust. Unless used with care and nuance, it is a term that is more likely to undermine than underpin a “rules-based order” in maritime Asia.
The U.S. position on the East and South China Sea disputes, as Defense Secretary Ash Carter and other officials have frequently reiterated in recent months, is that it opposes changes to the status quo made through force or coercion. Senior U.S. military and civilian officials have used this standard formulation frequently since mid-2013, most prominently in relation to the PRC’s East China Sea Air Defense Identification Zone (ADIZ), and its well-publicized island-construction project in the South China Sea.
Claimants in the disputed seas have also embraced the idea of defending the status quo from Chinese advances. The leaders of Japan and the Philippines on June 4 affirmed their opposition to “unilateral attempts to changes the status quo.” Vietnam maintains a slightly subtler position that stops short of outright opposition, as typified by Prime Minister Nguyen Tan Dung’s call for countries to refrain from “actions that would complicate the situation and change the status quo of rocks and shoals.”
Exploring China’s “Maritime Consciousness”, public opinion and nationalism
Posted: March 1, 2015 Filed under: Academic debates, Diaoyu, Global Times, PRC News Portals, South China Sea, State media, TV, Weibo | Tags: Chinese nationalism, Chinese public opinion, 环球时报, Diaoyu, Diaoyu Island, Diaoyu Islands, 舆论调查, 钓鱼岛, 西沙, 黄岩岛, Global Times, nationalism, online nationalism, online opinion, opinion polling, opinion surveys, Perth USAsia Centre, public opinion, south china sea, survey research, 南沙, 南海, 民意调查, 中国舆论, 中国民意 9 CommentsSomehow i’ve omitted to mention the report released in November on my first survey of Chinese public opinion on the country’s maritime disputes: Exploring China’s ‘Maritime Consciousness’: public opinion on the South and East China Sea disputes.
If you’re reading this blog you would probably have come across the report already. But since it’s based on on 1,413 conversations on the South China Sea and Diaoyu disputes, it probably does warrant a mention on this blog.
I’m doing a presentation and panel discussion on the report today (Monday, March 2) at the Australian Strategic Policy Institute, which Canberra-based readers may be interested in. I think the RSVP date has passed, but it’s probably a case of the more the merrier so if you’re keen i suggest clicking the link and getting in contact with ASPI.
Also based on the survey, a recent piece published on the University of Nottingham’s excellent China Policy Institute blog, as part of a special issue on nationalism in Asia. My contribution to that below:
~
Nationalism and Chinese public opinion
China Policy Institute Blog, February 3, 2015
By Andrew Chubb
Few terms in public political discourse are as contested, contradictory and downright slippery as nationalism. Deployed to describe an enormous variety of social movements, ideologies, popular attitudes, mass sentiments, elite policy agendas and even consumption patterns, use of the word carries with it a risk of stringing together superficially related phenomena with very different causes under the same label. The recently released results of a survey on the South and East China Sea disputes offer further reason for caution when approaching Chinese public opinion through the lens of nationalism.