Posted: March 1, 2015 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: Academic debates, Diaoyu, Global Times, PRC News Portals, South China Sea, State media, TV, Weibo | Tags: Chinese nationalism, Chinese public opinion, 环球时报, Diaoyu, Diaoyu Island, Diaoyu Islands, 舆论调查, 钓鱼岛, 西沙, 黄岩岛, Global Times, nationalism, online nationalism, online opinion, opinion polling, opinion surveys, Perth USAsia Centre, public opinion, south china sea, survey research, 南沙, 南海, 民意调查, 中国舆论, 中国民意 |
Somehow i’ve omitted to mention the report released in November on my first survey of Chinese public opinion on the country’s maritime disputes: Exploring China’s ‘Maritime Consciousness’: public opinion on the South and East China Sea disputes.
If you’re reading this blog you would probably have come across the report already. But since it’s based on on 1,413 conversations on the South China Sea and Diaoyu disputes, it probably does warrant a mention on this blog.
I’m doing a presentation and panel discussion on the report today (Monday, March 2) at the Australian Strategic Policy Institute, which Canberra-based readers may be interested in. I think the RSVP date has passed, but it’s probably a case of the more the merrier so if you’re keen i suggest clicking the link and getting in contact with ASPI.
Also based on the survey, a recent piece published on the University of Nottingham’s excellent China Policy Institute blog, as part of a special issue on nationalism in Asia. My contribution to that below:
~
China Policy Institute Blog, February 3, 2015
By Andrew Chubb
Few terms in public political discourse are as contested, contradictory and downright slippery as nationalism. Deployed to describe an enormous variety of social movements, ideologies, popular attitudes, mass sentiments, elite policy agendas and even consumption patterns, use of the word carries with it a risk of stringing together superficially related phenomena with very different causes under the same label. The recently released results of a survey on the South and East China Sea disputes offer further reason for caution when approaching Chinese public opinion through the lens of nationalism.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: April 20, 2014 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: Academic debates, China-Japan, Diaoyu, State media | Tags: anti-Japanese protest, Chinese foreign policy, Chinese internet, Chinese nationalism, Diaoyu Islands, 邱震海, Li Weizhi, online nationalism, Qiu Zhenhai, south china sea |

Instability threat: Anti-Japan protesters in Beijing, September 2012
The introduction to Phoenix TV host and international affairs commentator Qiu Zhenhai’s book, excerpted in Southern Weekend a couple of weeks back, reprises an important issue for everyone studying nationalism in China: to what extent should we really understand the phenomena that get labelled “Chinese nationalism” in those terms?
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: September 25, 2013 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: Academic debates, Article summaries, China-Japan, China-Koreas, China-Russia, China-US, CMS (China Maritime Surveillance), Diaoyu, Fake PLA generals?, FLEC & Ministry of Agriculture, PLA & PLAN | Tags: China Maritime Surveillance, Chinese media, Diaoyu Islands, hawkish faction, PLA hawks, Senkaku Islands, Sino-Japanese relations, Yan Xuetong, Yin Zhuo, 尹卓 |

CPPCC member Yin Zhuo at the 2013 ‘Two Meetings’ in Beijing, where he hosed down talk of war with Japan
PLA Marines on CMS boats patrolling Diaoyu hatching island-landing plans…’C-shaped Encirclement’ nothing but nonsense and online hype…China planned to attack Taiwan in 2006…America isn’t trying to contain China. What hostile imperialist could be dreaming up such baseless slander, inverting black and white, misleading the masses?
The answer is PLA Navy Rear Admiral Yin Zhuo 尹卓, at least according to someone who claims to have taken notes at his closed lecture in Chongqing on July 20. In addition to those admittedly rather more eye-catching claims, the translation appended below has raised once again (if only in my mind) the question of what the PLA’s appointed propaganda experts might really think about war, peace and strategy.
Admiral Yin is one of the most prominent PLA experts in the Chinese media, whose notable comments have included declaring the need for overseas PLA bases, sanctioning “violence” against the Philippines, arguing a Diaoyu war would be fought (and presumably won) in a “very short” space of time, and speculating about the prospect of Japanese warning shots over Diaoyu leading to military conflict.
At other times, however, such as during this year’s CPPCC, he has refused to speculate on future potential conflicts. He publicly refuted the idea of Japan and China inevitably fighting a war, echoing the argument General Liu Yuan was propounding at the time by stating that “only America would benefit” from such an occurrence. He has even been labeled “traitorous” after expressing disapproval of the idea of a more assertive stance in the South China Sea.
He is a princeling, the son of revolutionary hero Major-General Yin Mingliang, who held numerous positions in the PLA General Political Department’s political commissar system after 1949. Interestingly, he studied in France and returned in 1968 at the height of the Cultural Revolution to join the PLA. Aside from his membership of the CPPCC, he is the Director of the PLA Navy’s Informatized Warfare Experts Committee, and a member of the whole-army version of the same body. A recent provincial party magazine article stated that Admiral Yin has “participated in evaluation work for important national military strategy decision-making”.
All up, he is a relatively credible PLA policy voice compared to, say, Dai Xu.
He started appearing on CCTV in 1999, and in 2004 the PLA gave him the task of hosting a new CCTV military affairs program Military Picture Matching 军情连连看. Then, with the approval of the CCP Central Propaganda Department and GPD Propaganda Dept, Yin Zhuo obtained the titles of “CCTV special commentator” and “executive external propaganda expert” — the latter issued by then-GPD Director Gen Li Jinai.
So here, it seems, is a genuine PLA military thinker, a princeling thoroughly plugged into the policy-making system — who also just happens to be one of its most experienced and trusted propaganda operators.
Based on the following summary of his lecture, presented in the form of 30 points, it was quite a tour-de-force, with a broad scope, insight, inside knowledge and nuance (though my rough, cursory translation may obscure that).

On July 20, under invitation from China Mobile, Yin Zhuo came to Chongqing for a lecture titled ‘China’s security circumstances and the Diaoyu Islands issue’. The weather was favourable for Yin Zhuo’s two-day visit, as the temperature happened to drop from around 38C to 30C, and the air quality improved somewhat. In addition, the venue was at the foot of Jinyun Mountain, in nice surrounds with plenty of foliage, giving Yin Zhuo a good impression.
I was fortunate enough to be there. Because no recordings or video were allowed, I used a pen and paper to record the following main points, which I present as follows:
1. . . . America’s top priority in its quest to stay world hegemon is to disintegrate Sino-Russian relations.
2. America is extremely strong and China will be in a position of weakness until at least 2030. To escape the US’s pressure China must avoid its strengths and attack its weaknesses. . . .
3. America faces 3 problems, which are its weaknesses: declining politico-economic status, reduced ability to control the world geopolitically, and weakening alliances esp. in Asia-Pacific.
4. China was planning to attack Taiwan in 2006.
5. America and China have competition and confrontation, but confrontation is the main part . . .
6. China’s national strategy is to dig deeply to undermine the US, store up grain, and slowly seek to be king [modifying Mao Zedong’s 1970s dictum, “Dig deep holes, store up grain, do not seek hegemony 深挖洞,广积粮,不称霸].
7. . . . Some within the state and within the military think China can fight a war for the Diaoyu Islands and South China Sea to break out of America’s blockade, but [Yin Zhuo thinks] China should never underestimate America’s desire to attack us. . . . China can’t rely on America not wanting to get involved, we can’t even rule out the US using nukes.
8. Productive forces are still the element driving historical development. . . .
9. The wars of the 20th century and the Cold War caused a great deal of military technology to be converted to civilian use, spurring the information industries. . . .
10. Combined together, points 8 & 9 mean have led to America’s realignment towards the Asia-Pacific. As a capitalist country its national strategy must serve domestic economic development. Therefore, America’s strategic realignment is an inevitable trend, and one borne of the need to lead the Asia-Pacific, and is not directly aimed at China.
11. The PLA’s construction programme is geared towards winning a high-intensity conventional war under informatized conditions. This is an excellent approach but has its limitations.
12. In the Asia-Pacific region America lacks staunch allies, its military actions rely on NATO or itself.
13. The Snowden affair shows that freedom, democracy and human rights count for shit with the American people when faced with actual threats.
14. There are many East Turkestan [Xinjiang] terrorists fighting with Al-Qaeda, with around 1400 having received training. This is a threat to China domestically.
15. America is being opposed on a global scale by Islamic organizations. This will continue because the US is controlled by Israel [at least, on the Palestinian issue], so that problem can never be solved.
16. The US deliberately left Diaoyu to Japan in order to maintain Sino-Japanese enmity, “like Kashmir”.
17. The Japanese are increasingly right wing . . . they blame China for their prolonged recession.
18. Japan’s political system is gridlocked . . . under those circumstances we cannot rule out extremists taking control.
19. Economics is the best area for China to oppose the US. Make free trade agreements with neighbouring countries . . .
20. [Yin Zhuo is] unhappy with the feeble behaviour of the Department of Selling Out the Country [ie. the Ministry of Foreign Affairs]
21. Prepare to deal with Japan two-handed, we will not actively provoke armed confrontation but if Japan does then we will take a hardline stance and make them feel more pain than us in order to avoid an even greater conflict.
22. This year there have been marines on board CMS Haijian [now China Coast Guard] boats on patrols to Diaoyu, making contingency plans for landing on the islands. Also, there are a great many officers and men 官兵 applying to transfer 专业 to join them [I’m not sure if he means the Coast Guard or Marines?].
23. The [indigenous] large transport [plane] is progressing smoothly, design may be complete by 2015.
24. The C-Shaped Encirclement of China that gets hyped up online is nonsense. During the Cold War the US network of alliances, that was a real C-shaped encirclement. Nowadays the circle simply does not exist.
25. The ‘String of Pearls’ plan in the Indian Ocean is also nonsense. . . . China’s ports in the Indian Ocean are for civilian use.
26. Gwadar is an excellent port, but not suitable for building a military base due to the militant extremists in the area. We would be sending our troops there to serve as hostages.
27. China’s Indian Ocean strategy is focused on East Africa. It’s basically a blank slate out there.
28. The success of the Western development strategy depends on it being self-supporting, the Eastern provinces cannot support it long-term. The keys to making this happen are the sea links out of Yunnan and Tibet, and linking Xinjiang with Central Asia . . .
29. Our military modernization is progressing smoothly.
30. In the drawing of maritime boundaries with neighbouring countries [Vietnam and South Korea?] we have lost out badly.
I am inclined to think the above summary of his lecture is quite accurate. The lecture really happened, apparently in front of a businesslike audience of China Mobile VIP customers 全球通VIP客户, and the summary was posted online on July 21, the following day.[1]
Surprisingly perhaps, given the flagrant attack on Colonel Dai Xu’s flagship C-Shaped Encirclement thesis (Point 24), Dai Xu’s portal Hainan-sponsored website HaijiangZX.com posted the summary on July 26 under the headline, ‘Rare statement from Rear Admiral Yin Zhuo: Do not underestimate America’s determination to use force against China.
That could be explained as a result of HaijiangZX.com’s greediness for content (maybe Colonel Dai’s employees don’t bother to read the content of the articles they post). Or could it have been that Yin Zhuo knows C-Shaped Encirclement to be mere propaganda, irrelevant to policy? The fact that Yin described C-Shaped Encirclement as mere internet hype suggests he doesn’t consider it a serious analysis. On the other hand, it might have been a veiled putdown of a militant policy rival.
Interesting too that in Yin Zhuo’s speech the US is the main threat to China, but not because it has evil intentions, rather, because their interests are opposed. Does this imply Yin Zhuo is taking a kind of Yan Xuetong-style realist position, to respectfully disagree with the likely consensus behind General Qi Jianguo’s Study Times article in January, which argued that “points of common interest” between China and the US were likely to increase over the long term?
Some points in the speech seem to contradict what Yin Zhuo has said in the Chinese media. For example, in 2012 he wrote off nuclear weapons development as useless to China, yet here he talks about how the US might use them on China — thus rendering them crucial. He has also previously claimed that the US military is vulnerable to the PLA, stating for example that a US aircraft carriers can “definitely be sunk”. But in this lecture he emphasizes China’s weakness in comparison.[2]
What do you think — is this the capital-T Thought of a PLA princeling strategist, or is it more likely to be expertly delivered propaganda designed to look like “leak“, in order to influence what Chinese and foreign audiences believe about how the PLA sees the world? Or is it something else entirely?
~
[1] e.g. here and here; the first may have been this World of Warcraft forum here, from which it has been deleted.
[2] This might also reflect a CCP propagandist’s paradox: often, the more you characterize the US as a threat, the less military conflict looks like a good idea, but the less your people think military conflict is a good idea, the more susceptible they could be to the enemy’s psychological disintegration campaigns in the event that conflict occurs.

Yin Zhuo interviewed
Posted: August 13, 2013 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: Academic debates, Diaoyu, Fake PLA generals?, Global Times, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, PLA & PLAN, South China Sea, State media | Tags: Baidu Index, China-Philippines relations, Chinese foreign policy, Chinese media, Chinese military, Chinese nationalism, Chinese public opinion, 环球网, 环球时报, 罗援, Dai Xu, deterrence, Diaoyu, Diaoyu Islands, 钓鱼岛, 鹰派, 黄岩岛, Global Times, informatized warfare, Jamestown Foundation, Luo Yuan, military propaganda, PLA hawks, propaganda, scarborough shoal, Senkaku, Senkaku Islands, Sino-Japanese relations, south china sea, 忧患意识, 戴旭 |

Here is Part 2 on the PLA hawkish faction from China Brief, with added links to sources, and a couple of graphs from the utterly awesome Baidu Index (big hat tip to Kaiser Kuo).
I’d also like to add my thanks to Xuan Cheng, John Garnaut, James Barker, Mark Stokes and Taylor Fravel for discussions and tips on this topic. They don’t necessarily agree with the content of the article.
~
Publication: China Brief Volume: 13 Issue: 16
August 9, 2013
By: Andrew Chubb
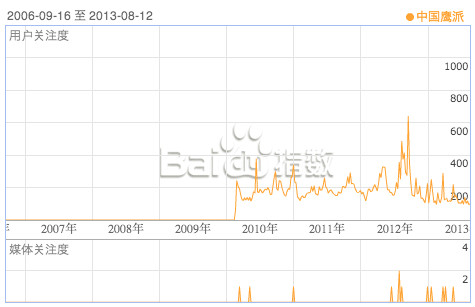
Rise of the hawks: searches for “China hawkish faction” by logged-in Baidu users since 2008. I’m requesting further info from Baidu regarding the extremely low pre-2010 numbers. One point that can be made with confidence is that user interest in the “Chinese hawkish faction” peaked during the Scarborough Shoal and (especially) Diaoyu Islands crises.
If outspoken Chinese military officers are, as Part One suggested, neither irrelevant loudmouths, nor factional warriors, nor yet the voice of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) on foreign policy, and are instead experts in the PLA-CCP propaganda system, then what might explain the bad publicity they often generate for China? This article explores how the activities of China’s military hawks may contribute to the regime’s domestic and international goals. On a general level, the very appearance of a hawkish faction—the “opera” that Luo Yuan has described—serves the domestic purposes of promoting national unity (Global Times, May 4). By amplifying threat awareness and countering perceived Western plots to permeate the psyche of the Chinese populace and army, the “hawks” direct public dissatisfaction with the policy status quo away from the system as a whole.
In specific crises, such as the standoff at Scarborough Shoal last year or in the wake of the Diaoyu Islands purchase, hard-line remarks from uniformed commentators serve to rally domestic public opinion behind the prospect of military action, instil confidence in the PLA’s willingness to fight over the issue and deter China’s adversary. By amplifying the possibility of otherwise irrational Chinese military action and inevitable escalation should Beijing’s actions be interfered with, they have contributed to a thus-far successful effort to convince the Philippines and Japan to accept the new status quo around Scarborough Shoal and the Diaoyu Islands.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: July 29, 2013 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: Academic debates, Diaoyu, Global Times, PLA & PLAN, PLA Daily, TV | Tags: CCTV, China Brief, Chinese foreign policy, Chinese military, civil-military relations, 罗援, 罗援少将, Dai Xu, Diaoyu Islands, external propaganda experts, Han Xudong, hawkish faction, Jamestown Foundation, Luo Yuan, military political work, military propaganda, Peng Guangqian, PLA hawks, PLA-CCP relations, propaganda, south china sea, Susan Shirk, Wang Jisi, Yin Zhuo, Zhang Zhaozhong, 军事对外宣传, 军事政治工作, 外宣, 尹卓, 张召忠, 彭光谦, 戴旭 |

Latest Jamestown China Brief piece, with links to sources:
~
Propaganda, Not Policy: Explaining the PLA’s “Hawkish Faction” (Part One)
By Andrew Chubb
The regular appearance in the Chinese media of People’s Liberation Army (PLA) figures calling for aggressive foreign policy causes controversy and confusion among foreign observers. The most sensational remarks usually are made by academics at PLA institutions. Foreign media routinely pick up sensational quotes from these military officers—such as Major General Luo Yuan’s repeated suggestion for declaring the Diaoyu Islands a Chinese military target range or Rear Admiral Zhang Zhaozhong’s recent call for a blockade of Philippine outposts in the Spratly Islands (Beijing TV/Huanqiu Wang, May 27)—and attribute them to senior military leaders, as their ranks seem to suggest (New York Times, August 20, 2012; TIME, Februrary 20; Tea Leaf Nation, February 25; South China Morning Post, March 6; Reuters, March 17). Operational commanders, however, seldom comment in public on policy issues. Prominent foreign policy analyst Wang Jisi has publicly complained about “reckless statements, made with no official authorization” which had “created a great deal of confusion” (Asian Wall Street Journal, July 1, 2012). In April, recently-retired deputy military region commander Wang Hongguang wrote military pundits had “misled the audience” and caused “interference with our high-level policy decision-making and deployments” (Global Times, April 20). This two-part series assesses who these outspoken PLA officers represent and the implications of their hawkish statements through an evaluation of their backgrounds, affiliations and statements on their work.
Debate about belligerent public remarks from military personnel often surrounds the extent to which they might represent the voice of hawkish PLA constituencies, pressuring the leadership to adopt more aggressive policies. Some analysts tend to dismiss such bluster as largely irrelevant on the basis that military media pundits have no operational military authority, despite their high rank. Others, however, emphasize how continued outspokenness by military figures presupposes high-level party or military support, and that they thus give voice to behind-the-scenes political struggles. A third view proposes that the hawks are the voice of the PLA as an institution, pushing the military’s policy preferences [1]. Analysis of scattered biographical information on the most prominent hawkish PLA media commentators, plus comments regarding their own work, suggests each perspective is partially right. None is a general in a conventional military sense, yet they are far from irrelevant. Their backgrounds, affiliations and positions, however, indicate their role probably has more to do with the regime’s domestic and international propaganda work objectives than political debates.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: April 29, 2013 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: China-Japan, Diaoyu, Global Times, PLA & PLAN | Tags: Chinese army propaganda, Chinese foreign policy, Chinese media, Chinese military, Chinese nationalism, Dai Xu, Diaoyu Islands, fire control radar, General Liu Yuan, Huanqiu, Huanqiu Shibao, Liu Yuan, Luo Yuan, Peng Guangqian, PLA, propaganda, radar incident, Senkaku, Wang Hongguang, Xi Jinping, Zhang Zhaozhong |

Increase vigilance: the reasonable conclusion of PLA pundits like Dai Xu?
[I spent hours on this post, then WordPress kindly lost it without a trace, hence this is a bit out-of-date, sorry]
The April 20 edition of the Huanqiu Shibao (Global Times) carried an article by recently-retired PLA Lieutenant-General Wang Hongguang, directly criticizing the Chinese media’s hawkish military commentators.
The article is brief — indeed so brief that the obligatory preface declaring support for the pundits’ patriotic mission does not even run to a full sentence:
In recent years, military affairs experts have frequently appeared on TV and in all kinds of publications, with the positive effect of strengthening the masses’ national defense awareness and arousing patriotism, but it cannot be denied that some have said off-key things, things that have misled the audience and been irresponsible.
Lt-Gen Wang, who now serves as Vice President of the PLA’s Academy of Military Science, made it quite clear that by “military affairs experts” he was referring to fellow PLA academics, particularly Zhang Zhaozhong, Luo Yuan, and of course Dai Xu.
It’s unusual to hear a PLA academic criticize his comrades in public; even more so for someone of such high rank. But most remarkable was Lt-Gen Wang’s claim that PLA academics’ war talk is “interfering” with the CCP-PLA leadership’s decision-making, citing the specific example of Sino-Japanese relations:
Some experts have inappropriately made comparisons of China and Japan’s military strength, claiming “China and Japan will inevitably go to war”, and that this “would not significantly affect our period of strategic opportunity”, [thus] inciting public sentiment and causing some interference with our high-level policy decision-making and deployments.
Wang Hongguang is in a position to know. Until recently he was Deputy Commander of the PLA’s Nanjing Military Region.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: March 19, 2013 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: China-Japan, Comment threads, Diaoyu, PLA & PLAN, PRC News Portals, Weibo, Xinhua | Tags: Chinese internet, Chinese internet news portals, Chinese public opinion, 罗援少将, Dai Xu, Diaoyu Islands, 钓鱼岛, General Liu Yuan, iFeng, Liu Yuan, Luo Yuan, Netease, online nationalism, phoenix, PHoenix online, PLA, public opinion, public opinion incident, Senkaku Islands, Sina, Sina weibo, Weibo, 刘源, 戴旭 |

Liu Yuan giving his March 14 interview

Luo Yuan
Over the past few weeks i’ve counted five instances of PLA General Liu Yuan publicly warning against military conflict with Japan over the Diaoyu Islands. If this puzzled the SCMP’s seasoned reporters, who described Liu as “hawkish” in a story quoting him saying, “The friendship between people in China and Japan is everlasting,” it was positively shocking for many of the Chinese internet’s e-nationalists. [1]
Actual serving General Liu Yuan is not to be confused with retired academic “Major-General” Luo Yuan (i’ll continue to put his rank in quotes to distinguish them), who was dumped from the CPPCC this month for being “too outspoken”.
That rationale was a bit ironic given he too has been oddly conciliatory on the Diaoyu issue of late. Not only did “Major-General” Luo categorically refute a Japanese media report that he had called for Tokyo to be bombed, he also seemed to deny he had ever suggested establishing a military presence on Diaoyu. And in one of his earliest Weibos, Luo raised a historical episode that seemed to imply that the US could secretly be trying to fool China into giving it a rationale for military intervention over Diaoyu:
In 1990, as Iraq massed military forces on the Kuwait border, the US ambassador told Saddam, “We do not take a position.” On July 31, US Assistant Secretary of State affirmed that “there is no duty compelling us to use our military”. As a result Iraq invaded Kuwait, under the belief that the US would not intervene, whereupon the US gained a great number of rationales for sending troops. From this we can see, the US wields not only high technology, but also strategic deception.
1990年,伊拉克在科威特边境集结军队时,美大使向萨达姆表示,“不持立场”,7月31日美助理国务卿在众院听证会上肯定“没有义务促使我们使用我们的军队”,结果,伊拉克在确信美不会介入的情况下,入侵科威特,于是,美获得了大量出兵的理由。由此可见,海湾战争,美国不仅玩的是高技术,还玩战略误导
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: February 25, 2013 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: China-Japan, China-Philippines, China-Vietnam, Diaoyu, People's Daily | Tags: Diaoyu Islands, diplomacy, East China Sea, Global Times, Japan-ASEAN, Japan-Philippines, Japan-US, Japan-Vietnam, Malaysia and South china SEa, Nguyen Tan Dung, People's Daily, Shinzo Abe, Sino-Japanese relations, south china sea, Truong Tan Sang, Vietnam, Vietnam-Japan, Zhong Sheng |

Japanese & Vietnamese Prime Ministers Nguyen Tan Dung and Shinzo Abe on January 16 in Hanoi
This post was originally published on the China Policy Institute Blog:
~
Between January 10 and 19 this year, Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and Foreign Minister Fumio Kishida paid formal bilateral visits to the Philippines, Singapore, Brunei, Australia, Vietnam, Thailand and Indonesia: seven countries in the space of 10 days. The diplomatic blitz illustrates the intersection of the East and South China Sea disputes, and the impetus this has given to Japan’s policy of deepening regional engagement since the early 2000s.
Six of Abe and Kishida’s seven destination countries were ASEAN member states, and three of them were parties to the South China Sea disputes. In fact, Taiwan aside, the only non-PRC South China Sea claimant state that Japan’s leaders did not visit was Malaysia, which continues to quietly extract hydrocarbons and develop tourism in the disputed area with little hindrance, thanks to its steadfast determination to avoid antagonizing Beijing.
Abe had actually wanted Washington to be his first destination after taking office, in line with his publicly stated intention to strengthen ties with the US, but Barack Obama was too busy to host a January summit. The hasty arrangement of Abe’s jaunt through Vietnam, Thailand and Indonesia — he set out on January 16, only nine days after being told Obama’s schedule was full — seems to suggest receptiveness to Japan’s advances in major ASEAN capitals.
Not surprisingly, the Philippines and Vietnam were the most openly enthusiastic about the Japanese leaders’ visits. Kishida arrived in Manila on January 9, exactly one month after Philippine Foreign Secretary Albert del Rosario told the Western media the Philippines would “very much” welcome a rearmed Japan free from pacifist constitutional constraints. This time Del Rosario took the opportunity to denounce the PRC’s South China Sea policy in probably the strongest terms yet seen from a serving minister, telling reporters after the meeting that the China was engaging in “very threatening” behaviour: “We do have this threat and this threat is shared by many countries not just by Japan.”
If the rhetoric sounded highly-strung, it was almost matched by the two countries’ actual actions. Del Rosario said Kishida had brought with him an offer of 10 brand-new patrol boats for the Philippines Coast Guard, later confirmed to be supplied under Japan’s Official Development Aid program. To put that in context, the Philippines Coast Guard only has 15 ships currently in service, plus 5 on order from France, so Japan is single-handedly increasing the PCG’s ship numbers by more than 30%.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: February 18, 2013 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: China-Japan, CMS (China Maritime Surveillance), Diaoyu, Global Times, PLA & PLAN, TV | Tags: CCTV, 环球时报, Diaoyu Islands, diplomacy, fire control radar, General Liu Yuan, Global Times, Japanese Maritime Self Defense Force, Liu Yuan, Natsuo Yamaguchi, PLA General Logistics Department, radar incident, Senkaku Islands, Sino-Japanese relations, 刘源 |

As seen on TV…well, not quite but almost
Apologies to anyone who may have visited in hope of new material in the past few weeks. This year I need to write a PhD dissertation so posts will be even more sporadic than usual. There are a number of unfinished ones in the pipeline that I really hope to get around to completing at some point, and I will try to also post some of the summary translations of significant PRC media articles and comment threads that I normally keep to myself.
What follows is a piece I wrote for the Jamestown Foundation’s China Brief which came out last Friday: Radar Incident Obscures Beijing’s Conciliatory Turn. This version here has the addition of links to the sources at the end.
Also, since there are no comments on the Jamestown website, I encourage anyone who wants to discuss to leave comments here on this post.
Thank you for tuning in and making this blog such a temptation to write on.
—
Radar Incident Obscures Beijing’s Conciliatory Turn Towards Japan
China Brief, Vol 13, Issue 4
February 15, 2013
On February 5, Japanese Defense Minister Onodera Itsunori told the world that a Chinese Navy frigate had pointed “something like fire-control radar” at a Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force (MSDF) destroyer some 100-150 kilometers north of the disputed Diaoyu/Senkaku Islands on January 30. He said the same may have happened to a MSDF helicopter on January 19, though this remained unverified (Daily Yomiuri, February 7; Sydney Morning Herald, February 7).
This marked the first direct involvement of People’s Liberation Army (PLA) Navy ships in the ongoing confrontations around the islands since Japan’s government purchased three of them from a private Japanese owner on September 10 last year. Accordingly, much reportage and analysis has characterized this as part of an ongoing series of escalatory Chinese actions in the East China Sea. Yet the radar incidents ran counter to a distinctly conciliatory trend since mid-January in China’s official rhetoric, diplomatic action, media discourse and even maritime activities.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: December 14, 2012 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: China's foreign relations, China-Japan, CMS (China Maritime Surveillance), Diaoyu | Tags: 18th CCP Congress, China leadership transition, China Maritime Surveillance, Chinese foreign policy, Chinese nationalism, CMS, Diaoyu Islands, great revival, Hu Jintao, PRC foreign policy, PRC maritime law enforcement, PRC-Japan, Senkaku, taoguang yanghui, western media, Xi Jinping, Xi Jinping foreign policy, Xi Jinping nationalism |

April, 2012: Vice President Xi Jinping Meets with the Japanese Association for the Promotion of International Trade Delegation
Last week the New York Times ran a story on how Ling Jihua’s attempt to cover up his son’s death in that Ferrari crash may have severely weakened Hu Jintao’s position during this year’s CCP leadership transition.
It might just be me and my island-centricness, but this story certainly didn’t seem to be following the inverted-pyramid rule, for only those readers who persisted to the very last paragraph (or read the Sinocism China Newsletter) would have learned that:
By September, party insiders said, Mr. Hu was so strained by the Ling affair and the leadership negotiations that he seemed resigned to yielding power. As Mr. Hu’s influence faded, Mr. Xi began taking charge of military affairs, including a group coordinating China’s response to the escalating row with Japan over disputed islands.
Given both the vital role Ling had played in managing the logistics of the General Secretary’s day-to-day activities, and the likely emotional toll of the death of a close associate’s son, this idea of a Human Jintao feeling the pinch is logical enough.
Although the Times‘ sources say Ling’s replacement as CCP General Office Director, Li Zhanshu, arrived in July, the public announcement of Ling’s reassignment from the post was only made on September 1. Then Noda reached his agreement with the Kurihara family to make the purchase on September 4. Could all this explain Xi Jinping’s lack of a public appearance between September 2 and September 12? If i were gearing up to take over as CCP General Secretary in a few months’ time and then found myself taking charge of the country’s response to a rapidly-escalating crisis, i’d have trouble finding time for photo ops.
Read the rest of this entry »











First Luo Yuan, now Liu Yuan: from one “public opinion incident” to another
Posted: March 19, 2013 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: China-Japan, Comment threads, Diaoyu, PLA & PLAN, PRC News Portals, Weibo, Xinhua | Tags: Chinese internet, Chinese internet news portals, Chinese public opinion, 罗援少将, Dai Xu, Diaoyu Islands, 钓鱼岛, General Liu Yuan, iFeng, Liu Yuan, Luo Yuan, Netease, online nationalism, phoenix, PHoenix online, PLA, public opinion, public opinion incident, Senkaku Islands, Sina, Sina weibo, Weibo, 刘源, 戴旭 | 9 CommentsLiu Yuan giving his March 14 interview
Luo Yuan
Over the past few weeks i’ve counted five instances of PLA General Liu Yuan publicly warning against military conflict with Japan over the Diaoyu Islands. If this puzzled the SCMP’s seasoned reporters, who described Liu as “hawkish” in a story quoting him saying, “The friendship between people in China and Japan is everlasting,” it was positively shocking for many of the Chinese internet’s e-nationalists. [1]
Actual serving General Liu Yuan is not to be confused with retired academic “Major-General” Luo Yuan (i’ll continue to put his rank in quotes to distinguish them), who was dumped from the CPPCC this month for being “too outspoken”.
That rationale was a bit ironic given he too has been oddly conciliatory on the Diaoyu issue of late. Not only did “Major-General” Luo categorically refute a Japanese media report that he had called for Tokyo to be bombed, he also seemed to deny he had ever suggested establishing a military presence on Diaoyu. And in one of his earliest Weibos, Luo raised a historical episode that seemed to imply that the US could secretly be trying to fool China into giving it a rationale for military intervention over Diaoyu:
Read the rest of this entry »