Comparison of Vietnam and China’s joint statements, 2011-2017
Posted: February 3, 2017 Filed under: China-Vietnam, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, South China Sea | Tags: arbitration, China-Vietnam, China-Vietnam joint statement, China-Vietnam relations, joint communique, Nguyen Phu Trong, nine dashed line, nine-dash line, Philippines vs China arbitration, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, South China Sea arbitration, UNCLOS, UNCLOS and South China Sea, Vietnam-China joint statement 2 Comments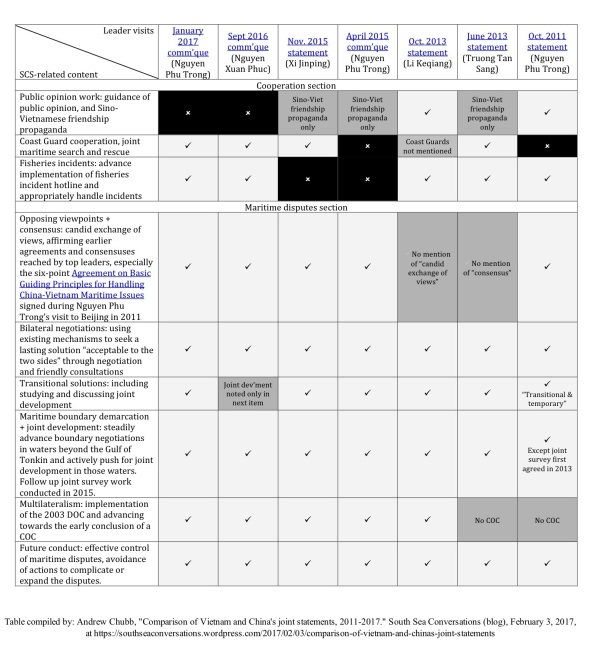
Comparison of Sino-Vietnamese joint statements since 2011 (click to enlarge). Links to sources: January 2017 communique (Nguyen Phu Trong visit to China); Sept 2016 communique (Nguyen Xuan Phuc visit to China); Nov. 2015 statement (Xi Jinping visit to Vietnam); April 2015 communique (Nguyen Phu Trong visit to China); Oct. 2013 statement (Li Keqiang visit to Vietnam); June 2013 statement (Truong Tan Sang visit to China); Oct. 2011 statement (Nguyen Phu Trong visit to China).
East Asia Forum has kindly published a piece from me on recent developments in Sino-Vietnamese relations. To supplement it, i’m posting here a table comparing the South China Sea-related elements of the last 7 joint statements between the two.
The comparative table was the basis for the article’s argument that General Secretary Nguyen Phu Trong’s visit to Beijing last month did not involve any softening of Vietnam’s position on the issue.
According to a knowledgeable Vietnamese source, there are three types of Sino-Vietnamese bilateral joint statements issued after high-level meetings. In ascending order of importance these are:
- Joint press release (联合新闻公报, thông cáo báo chí)
- Joint communique (联合公报, thông cáo chung)
- Joint statement (联合声明, tuyên bố chung)
These documents are often not released in English, and some of the translations that have appeared have been incomplete or unreliable, so the table above compares the Chinese full text as published by state media (links are in the caption area above).
The table also includes an item, not discussed in the EAF article for space reasons, on cooperation in public opinion work. In the 2011 joint statement, the two sides pledged cooperation on “strengthening public opinion guidance and management” – which, in the context of several weeks of anti-China protests through the middle of that year, was tantamount to a Vietnamese undertaking to dampen anti-China sentiments.
Interestingly, however, there has been no analogous item in the recent joint documents — even after another, even more intense, wave of anti-China sentiments burst forth in 2014 during the HYSY-981 oil rig standoff. Its omission from subsequent documents might indicate an acceptance on China’s behalf of the strength Vietnamese nationalist sentiments that flow in its direction at times of heightened tensions. Perhaps also an acknowledgement that Hanoi is already doing what it can to promote Sino-Vietnamese friendship? Any other readings?
The EAF piece is reposted below. Based on some early feedback, i should have been clearer that in suggesting . . .
China may have pulled back from its pursuit of particular claims that have no basis in international law
. . . i do not mean the PRC has seen the light and is abandoning all claims deemed unlawful in the UNCLOS arbitration. Just that there are some unlawful aspects of China’s claims that it is no longer pushing, and this has removed some of the major drivers of Sino-Vietnamese tensions.
As always, further comments, arguments, additions and corrections are much appreciated.
China’s expanding Spratly outposts: artificial, but not so new
Posted: June 19, 2014 Filed under: China-ASEAN, China-Philippines, China-Vietnam, CMS (China Maritime Surveillance), South China Sea, Western media | Tags: artificial islands, CCTV, China, China Coast Guard, China Coastguard, China Marine Surveillance, china maritime dispute, China Maritime Surveillance, Chinese foreign policy, 礁堡, 高脚室, 高脚屋, First Island Chain, Gulf of Tonkin, HYSY-981, Johnson Reef, Johnson Reef South, Mabini Reef, Nanhai-9, New York Times, paracel islands, Paracels, reclamation, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, Spratly, spratly islands, UNCLOS, western media 3 Comments
China’s Johnson Reef (赤瓜礁) reclamation project, as photographed by the Philippines Navy (click for source)
Here’s another attempt at what a blog post probably should be: a short comment on some things i’ve read online. It’s about the New York Times’ report this week on China’s island reclamation work in the Spratlys, which i think missed some important background context to China’s activities.
The subject, in summary:
China has been moving sand onto reefs and shoals to add several new islands to the Spratly archipelago, in what foreign officials say is a new effort to expand the Chinese footprint in the South China Sea. The officials say the islands will be able to support large buildings, human habitation and surveillance equipment, including radar.
This island reclamation is the latest in a long line of measures China has taken since the early 1980s to strengthen its presence in the Spratly Islands, which it views as crucial due to their proximity to China’s sea approaches, as well as present (fisheries) and future (energy) resource bounties.
China-Vietnam clash in the Paracels: history still rhyming in the Internet era?
Posted: May 7, 2014 Filed under: Academic debates, China-Vietnam, Global Times, PRC News Portals, South China Sea, Xinhua | Tags: Chinese foreign policy, Chinese internet censorship, Chinese internet news portals, Chinese media, Chinese nationalism, CNOOC, HYSY-981, internet censorship, Netease, oil and gas, online opinion, paracel islands, Sina weibo, Sino-Vietnamese incidents, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, Weibo, 海洋石油-981, 中越撞船 11 Comments
Vietnamese diplomats are saying Chinese and Vietnamese ships collided today in the disputed Paracel Islands, where China has stationed the massive oil and gas drilling platform HYSY-981. The incident may be in some ways unprecedented as the first time China has attempted to drill for hydrocarbons in a disputed area of the South China Sea. But it also resonates with the past in some surprising ways, from the PRC’s initiation of the incident, to Vietnam’s response, and even the information environment facing the two sides.
Creative tensions and soft landings: Wang Yizhou explains China’s foreign policy agenda
Posted: December 17, 2013 Filed under: Academic debates, China's foreign relations, China-ASEAN, China-Japan, China-US | Tags: Carnegie-Tsinghua Center, China-Japan, China-North Korea relations, China-US relations, China-Vietnam, China-Vietnam relations, Chinese foreign policy, Chinese foreign policy scholars, Chinese strategy, creative tensions, 王逸舟, New kind of great power relations, north korea, Paul Haenle, peripheral diplomacy, PRC foreign policy, Sino-American relations, Sino-Japanese relations, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, Wang Yizhou, Xi Jinping foreign policy 4 CommentsPeking University Professor Wang Yizhou, one of China’s top foreign policy scholars, did an interview for the excellent new Carnegie-Tsinghua podcast last month (Part 1 and Part 2), covering a very broad sweep of China’s emerging foreign policy, regional strategy, territorial disputes, global role, and bilateral relations with the US.
His main points are noted below, starting with regional strategy and China’s maritime territorial disputes. I’ve just done this as an exercise to try to better grasp the significance of what Wang says; for most people it’s probably better to just go listen to the podcast. The italicized blockquote bits are a mix of direct quotes and paraphrasing.
~
Xi’s task: a “soft landing” for the South China Sea dispute
Dai Xu Thought?
Posted: August 29, 2013 Filed under: Academic debates, China-Vietnam, Fake PLA generals?, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, PLA & PLAN | Tags: Dai Xu, People's Tribune, PLA hardliners, PLA hawks, PRC foreign policy, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, spratly islands, 戴旭, 人民论坛 1 CommentIn case i dont make it clear enough, a lot of what I write is speculative, my aim is to try understand these things as best I can, and I would really appreciate any alternative explanations, identification of shortcomings, points of disagreement, criticisms, biases identified, etc etc.
I am sure some of the interpretations I come up will turn out to be mistaken and/or incomplete, and although I hope some turn out to be right, it’s far from the end of the world if i’ve got it all wrong. It will be still have been worth the effort just to eliminate all those mistaken lines of thinking.
One idea i’ve been getting closer to ruling out is that Dai Xu and Luo Yuan aren’t serious PLA strategic thinkers. I think they are both propagandists and strategists. One sign is their publication in genuine journals like World Economics and Politics 《世界经济与政治》 (published by CASS), Contemporary International Relations 《现代国际关系》 (published by the MSS-affiliated CICIR), Contemporary World 《当代世界》 (CCP International Department), World Outlook 《国际展望》 (Shanghai Institute of International Relations), and Teaching and Research 《教育于研究》 (Renmin University).[1]
While they are nominated as propaganda experts,[2] they could still spend the bulk of their time in the world of thought rather than propaganda. Even Dai Xu, whose gigantic mass media output suggests he could probably spare little time for academic work,[3] stated in 2009 that he does both internal and external work — that is, both thought 思想 and propaganda 宣传.
The difference between the two, as he said in his lecture to the PLAAF Political Academy in Shanghai, is that “in thought, anything goes, but propaganda has discipline”. This was, he said, the most important lesson he learned at the academy, his alma mater. There may be a large degree of crossover between Dai Xu Thought, and Dai Xu Propaganda — they may in fact be the same, except that the latter is presented and attenuated according to propaganda imperatives.
What follows, then, is something long overdue given the amount of attention i have focused on the propaganda side of Dai Xu and Luo Yuan’s work: a partial translation of an essay that i think may come close to representing what Dai Xu really thinks, as a strategist, on the South China Sea issue. It might not be pure thought…if there was such a thing, probably the only place it could reliably be identified would be in internal-circulation articles. But People’s Tribune Frontiers 《人民论坛.学术前沿》 appears a reputable (though recently-founded) CCP journal produced by the People’s Daily group, without any attempt at mass appeal, suggesting the audience would be mainly Party members and scholars, and perhaps soldiers and policymakers too.[4] In other words, it could conceivably be part of the “internal work” that Dai says he does — Dai Xu Thought.
The article is titled ‘ “Attacking the Enemy before It is Fully Prepared”: A Petition for Changing South China Sea Strategy (“兵半渡可击”:南海战略万言书)’, and is freely available via a Hainan-based website called ‘Maritime Domain Online’ (海疆在线) that i suspect is run by the Hainan Maritime Security and Cooperation Institute that Dai Xu directs.
As the title suggests, Dai makes specific policy suggestions, based on a contention that China has a rapidly-closing “window of opportunity” to “resolve” the South China Sea issue, and should therefore act sooner rather than later. Notably, however, one of these suggestions is to call for the total demilitarization of the South China Sea’s disputed areas. He advocates “intensifying economic exploitation” but also “welcoming cooperation”. He argues China should rally round the nine-dash line and avoid any involvement of UNCLOS, but he also seems to advocate negotiations. Dai’s calls for military preparations and willingness to use force to back up the assertive actions he suggests, but his emphasis is on deterrence and willpower.
Big thanks to Xu Shaomin for suggesting the article.
Here is the abstract, followed by a translation of the section in which Dai makes his policy suggestions with some thoughts on those policies appended, and finally a brief consideration of some implications for the explanations i’ve recently offered for the public activities of PLA “hawks” like Dai.
~
“Attacking the Enemy before It is Fully Prepared”: A Petition for Changing South China Sea Strategy
By Dai Xu
People’s Tribune [Academic] Frontiers 《人民论坛--学术前沿》
ABSTRACT: An indisputable fact is that China is facing unprecedented challenges presented by the South China Sea issue. The said issue has been internationalized, and will soon become a focus of international politics. The South China Sea is of great significance for China’s development and security. With the development of this issue, Vietnam will rise to be China’s major concern. To successfully resolve this issue, China needs to devise a “protracted war” strategy; use the current crisis as an opportunity for a shift in military strategy; set up an interdepartmental coordination committee; and materially change its current South China Sea policy.
[…]
Specific suggestions to resolve the South China Sea issue
| (translator’s thoughts) | |
| (1.) Institute determination to resolve the issue, and commence joint preparations in all areas. At present America is not ready and has not properly armed those small countries, and external powers like Japan have not substantively entered the dispute. China must seize and occupy the strategic heights of the future, and cannot let it become the Yellow Sea again. |
The idea of (1) gets to the heart of the paper’s debatable but nonetheless logically defensible premise: namely, that China has a 5-10 year “window of opportunity” while the US is bogged down in the Middle East. I don’t really understand this Yellow Sea reference. |
| (2.) Unite thinking, resolutely stick to the nine-dash line. The nine-dash line is the legal basis for China’s ownership of the Spratlys, and we absolutely cannot renounce it. We cannot make UNCLOS the main note of negotiations. |
The strong defence in of the nine-dashed line as “legal basis” of China’s claim in (2), and associated rejection of UNCLOS, is somewhat surprising, considering that elsewhere Dai is quite keen on transparency and clarity of intentions. Why not clarify the claim?[5] China could continue to claim all the land features within the nine-dash line, and actually be in accordance with UNCLOS. China’s real reason for not clarifying may be that it would entail enforcement under Chinese law, which the CCP may not be keen to commit to at this point. If so, could this particular argument of Dai’s be aimed at maintaining morale, while avoiding that sort of dangerous bind? |
| (3.) On the level of unified thinking, eliminate fear of America. Surveying US-Russian relations one can see that America respects strength. Russia halted the US [Cold War] strategic attack in Southeast Asia, and stopped the expansion of NATO beyond Ukraine and Georgia. We cannot say that [Deng/Jiang’s doctrine of] “lying low 韬光养晦” is incorrect, but China is unaware of how to “loot a burning house 趁火打劫”. China must have an awareness of global strategic games. China should participate in South American affairs, the scramble for Arctic resources, Middle East affairs, African affairs, and force the US to encircle us all around the world, “saving Zhao by besieging Wei 围魏救赵”, thus reducing the pressure on our doorstep. Increase cooperation with Russia, cooperate on the Kurils issue to draw Japan northward, and weaken US military allies. |
The idea of causing headaches for the US around the world to relieve the pressure on China’s periphery, as set out in (3), employs a coherent (if somewhat unhealthy when viewed from outside) strategic logic. I’m not going to pretend to know what’s best for China, but the multi-departmental group mentioned in (4) also seems to make sense. |
| (4.) Establish a multi-departmental South China Sea coordination small group. The group would be jointly composed from the military, academia, State Oceanic Administration, Hainan Provincial Government, and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. It should change the situation of the MFA being under stress from dealing with the complicated South China Sea situation alone. It should coordinate all the departments relevant to the South China Sea. |
(4) contains a clear argument for reducing the MFA’s power in South China Sea policymaking, via an indirect but unmistakable criticism of both the prominence of the Foreign Ministry’s role, and the job it is doing. Dai’s apparent perception of the MFA as dominating South China Sea policy is in stark contrast to various foreign analysts who have written of the weakness of the MFA, fragmentation in China’s foreign policymaking, especially on maritime disputes. |
| (5.) Major adjustment must be made to South China Sea policy, prioritizing [economic] exploitation [6]. Since diplomacy being unable to resolve the issue, and our country is unwilling to go to war lightly, all that remains is to greatly intensify economic exploitation. Our country’s South China Sea policy should be adjusted to: sovereignty is ours, intensifying exploitation, welcoming cooperation, not fearing controversy, striking against provocation. Exploitation is central. In order to reduce the concerns of the international community, China’s exploitation should proceed with the primary objective of serving the world. For example, constructing an international shipping depot, and an international tourism and sightseeing spot. To this end, a South China Sea Special Zone should be established, as a maritime screen that also performs the functions of economic national defense 经济国防. |
Dai’s Hainan connections keep stacking up. It seems likely that he is to some extent speaking on behalf of the Hainan Provincial Government, especially with the strong advocacy of economic development projects in (5). How novel is “economic national defense 经济国防“, meaning economic activities for national defense purposes, in the Chinese context and more broadly? |
| (6.) Call on all countries’ militaries to withdraw from the South China Sea. Because Vietnam and the Philippines’ garrisoning of troops has affected regional shipping security, China should call for all countries to pull out their militaries simultaneously. This way, China can claim the moral high ground. |
Dai in (5) describes China being “unwilling” to go to war lightly as a “situation” that has left massive resource exploitation as the only option — which sounds like a (grudging?) admission that direct military action is off the policy table. Then in (6) he actually advocates the pullout of all military forces from the area, apparently including China’s. |
| (7.) Prepare properly for war [with Vietnam]. China should, at the appropriate time, adjust its strategic focus, and conduct far-sighted and realistic research on the South China Sea. Make every kind of war preparation in the South China Sea area, especially for war-fighting 作战 against Vietnam. As soon as conflict commences, Vietnam’s facilities must be totally destroyed, and its ports blockaded. |
Dai is very harsh and provocative regarding Vietnam, for example in (7). What is Dai’s problem with Vietnam? Or could it be Hainan’s problem with Vietnam? |
Enacting strategic containment of Vietnam is beneficial to the long-term stability of the South China Sea region, and also to improving our country’s overall security situation.
~
Implications for ‘Propaganda, Not Policy’
While some of these arguments may be attenuated from Dai’s mass media statements, he really does appear to be attempting to pushing for policy change in the South China Sea, which at a glance spells trouble for the ‘Propaganda, Not Policy’ explanation i’ve been proposing. Yet, contrary to what some angry military enthusiasts assume, the Propaganda Not Policy argument does not necessarily imply Dai Xu doesn’t mean what he says. He may mean most or all of what he says publicly, but he only says it if and when it accords with the priorities of his superiors in the military propaganda system.
Alternatively, considering the likely target audience of the People’s Tribune Frontiers, an article such as this could be aimed at the masses of cadres, officers and possibly soldiers. David Cohen discussed in the most recent China Brief how the constitutionalism debate could be intended to rally cadres to be vigilant and toe the line. It’s plausible that this has a similar intent.
What’s different about this is that it has been published in a forum for genuine scholarly debate over policy, rather than a mass medium. Perhaps all that is certain about this possible piece of Dai Xu Thought, is that he was attempting to influence the Party and academic policy debate within China. Whether the ultimate aim of that was to institute the specific policy actions, or to shift the mindset of the readers — such as by raising the vigilance of cadres and perhaps soldiers — is unclear to me. What do you think? What are the other possibilities that i’m overlooking?
~
[1] Other notable titles that Luo and/or Dai have been published in include Party & Government Forum 《党政干部文摘》 (Shanghai and Central Party School versions), World Affairs 《世界知识》 (Ministry of Foreign Affairs), Contemporary Military Digest 《当代军事文摘》 (PLA Publishing House), Aerospace Knowledge 《航空知识》 (China Aviation Society). Found using CNKI database.
[2] I’m going to leave out the “external” from the “external propaganda expert” title, as it risks confusing the issue. Military external propaganda, as noted here, is not just about foreigners, and in fact may be overwhelmingly domestically directed, even as it serves international goals of public opinion warfare.
[3] Unless he has a team of ghost writers…?! His book publishing, however, has indeed slowed down in recent years.
[4] Can anyone enlighten me as to the People’s Tribune (Frontiers) target readership and/or purposes?
[5] Sovereignty over merely the largest two or three of the Spratlys — those with fresh water and therefore at least arguably inhabitable — would generate exclusive economic rights covering most of the area within the nine-dash line.
[6] 开发, aka “development”.
Professor Chen Jie explains the Spratly triangle
Posted: August 27, 2012 Filed under: Article summaries, China-Philippines, China-Vietnam | Tags: 1988 Spratly Battle, Chen Jie, China-Philippines relations, China-Vietnam relations, 陈杰, Jie Chen, SBS Radio, Sino-Vietnamese relations, spratly islands, Vietnam-Russia 3 Comments–Note: apologies to email subscribers for the incomplete draft sent out just now. I didn’t realise the Iphone app could interpret an errant finger swipe as an instruction to “publish now”. I will hopefully finish it off today after i’ve spoken to some more friends.–
In the dispute over the Spratly Islands, a China-Vietnam-Philippines triangle of active claimants has taken shape, with external great powers the US, India, Russia and perhaps even Japan lurking, anxious about possible trouble and eager to seize any strategic opportunity. The interview translated here, recorded in November 2011 following several months of intense diplomatic maneuverings, offers an excellent recap of how we arrived at the more direct competition of 2012, as well as touching on the issues raised in the previous post.
The three sections, indicated by the host’s questions in bold, canvass:
- Vietnam’s diplomatic triple-dealings with China, India and the Philippines in October 2011;
- The connections between great-power politics and Vietnamese ruling-party politics; and
- The difference between the Philippines’ and Vietnam’s approaches.
The interview was broadcast by the multilingual Australian SBS Radio with with Jie Chen 陈杰, Professor of International Relations at the University of Western Australia. Professor Chen is an expert on Southeast Asian and Chinese foreign policy who is supervising my PhD project.
Would China and Vietnam want a fight?
Posted: August 23, 2012 Filed under: China-Russia, China-US, China-Vietnam | Tags: 1988 Spratly Battle, Cam Ranh Bay, China-Vietnam relations, Gazprom, Johnson South Reef Skirmish, legitimacy, PLA, s, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, spratly islands, Truong Tan Sang, US-China relations, Vietnam-Russia 8 CommentsBill Bishop (@niubi) raised an important point in yesterday’s Sinocism:
economic problems in china, economic problems in vietnam. a skirmish in the south china sea might be a distraction and an economic fillip for both?
This is worth thinking through carefully, and i would be most obliged if readers could pick out the holes in my logic and knowledge.
My propositions are
- that China could benefit from such a fight, though it might be too afraid of US opportunism to grasp them; and
- even if China was indeed up for a fight, it would take both of them to tango, and Vietnam wouldn’t be keen.
China would be the likely beneficiary of a live-fire skirmish involving the PLAN, for under that pretext China could evict Vietnam from one or more islands of its choosing. That would be the first time the People’s Republic had ever controlled an island in the Spratly Archipelago.
Possession of a single island in the Spratlys would hugely enhance the position of the People’s Republic strategically, logistically, and legally. What is more, i dare say it might be viewed as a glorious success by some people in China.
“Retrieving” 收复 a Spratly island by evicting an opponent is perhaps the one action that could actually impress the Chinese public and bolster the party’s “nationalist legitimacy” at home.
Despite possessing a much better navy and air force than the Philippines, i think Vietnam would be a more appealing target for an island “retrieval” simply because there would be no issue of the US becoming involved via treaty obligation. This is also reflected in the fact that Vietnam is the only country the PRC has attacked in the South China Sea.
The best opportunity for the PRC to make a move like this would be a clear-cut instance of Vietnamese aggression. A flagrant attack a PLA Navy boat by Vietnamese fishermen might constitute a justfiable rationale for an island battle. If multiple attacks happened (or could somehow be made to happen) then China could instruct its military to go looking for the attackers on one or more of the Vietnamese-controlled Spratly Islands.
Would America step in to prevent China from gaining such prime a foothold as a Spratly Island? I think not, as long as China could convince the world that Vietnam had started the incident.
On the other hand, even if Vietnam were to oblige by recklessly attacking the PLA Navy, the risk for China would be that the US could use the ensuing PLA retaliation as an opportunity to assert itself in the region, and perhaps even to bring the PLA’s development “under control”. From my hypothetical Chinese military perspective, the US could conceivably unleash its considerable (though much-degraded by Saddam’s WMDs) narrative-building powers to convince the world that China was to blame for any clash — even, or perhaps especially, a clash brought about by Vietnam, under US encouragement.
So while China would stand to gain a great deal from a skirmish, it could still be deterred by its own belief in the US’s evil intentions and opportunism.
Vietnam, meanwhile, has its good friend Russia increasingly tangled up with its own fortunes through a range of energy development partnerships (“such as Vietsovpetro, Rusvietpetro, Gazpromviet and Vietgazprom”), and Russia may soon be present in Cam Ranh Bay, which Vietnam has offered as a the site of a Russian supply and maintenance base.
Xinhua’s Moscow-datelined report from August 27, ‘Vietnam declines to give Russia exclusive rights to naval base‘ (my emphasis) appears to be clutching at straws trying to find a positive angle for China; President Truong Tan Sang’s 5-day visit to Russia last month appears to have been a riproaring success. The reason Russia will not have exclusive rights, is of course that Vietnam has invited the US military to use Cam Ranh Bay too.
The Chinese media have frequently accused the US of trying to embolden China’s co-claimants into making provocations. From Hillary’s famous declaration of national interest, to (non-combat) military exercises in July 2011, to Leon Panetta’s visit to Cam Ranh Bay in June this year, the US has definitely been pushing things forward with Vietnam too.
In the event of a skirmish with China, however, Vietnam still couldn’t count on support from either the US or Russia, both of which continue to have enormous national interests in maintaining peace with the People’s Republic.
When it comes to the South China Sea, Vietnam is the only country that has ever actually tried to fight with the PRC there — and that did not end well (see video at top). Yet Vietnam’s position in the Spratlys remains very favourable compared to the People’s Republic’s, occupying at least six islands and more than twenty reefs and atolls, and an estimated 2,000 troops posted as of 2002. Why would they risk this, with possession is (probably) nine-tenths of the law?
To me, this all points to Vietnam being determined to avoid serious escalations, even as the US bolsters its position in the region.
“A certain neighbouring country” returns to the South China Sea dispute
Posted: June 3, 2012 Filed under: China-Vietnam, Comment threads, FLEC & Ministry of Agriculture, Global Times, PRC News Portals, TV, Xinhua | Tags: China Fisheries, China Fisheries Law Enforcement Command, China-Vietnam, Chinese internet, 环球时报, FLEC, Global Times, Huanqiu Shibao, Ministry of Agriculture, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, yuzheng 310, 农业部, 渔政310, 中国渔政 4 Comments
14 Vietnamese fishermen detained by China from May 16 to 21 have their first meal following their release
It was as though they were playing tag-team† in a WWF wrestling show. Just as the China-Philippines tensions started to diminish, who should pop up to disturb China’s peaceful claims? Why, “a certain neighbouring country”, of course.
When Philippines President Benigno Aquino III welcomed, and indeed matched, the PRC’s yearly South China Sea fishing ban, Vietnam’s Foreign Ministr labelled it “invalid”.
On May 24 the Vietnamese held another press conference at which spokesman Luong Thanh Nghi said that China had detained two Vietnamese fishing boats in the Paracel Islands on May 16 (for some reason this VietnamNet report says the incident occurred in the Spratlys), and held the 14 crew until May 21. As soon as China officially advised Vietnam about the incident on May 21, according to spokesman Luong, the Vietnamese side lodged a strong diplomatic protest against the “severe violation of the sovereignty, sovereign rights and jurisdictions of Viet Nam”.
There are plenty of details in this English-language Vietnamese media report…
Vo Minh Quan, 42, the captain of QNg 50003TS boat, said the fishermen went to sea on May 2. Fourteen days later, at 9 am on May 16, a Chinese ship coded 306 suddenly appeared and seized the boat and the crew.
The foreign ship later captured the QNg 55003TS boat piloted by captain Tran The Anh and then escorted the two boats with all their crewmembers to Phu Lam [永兴, Woody] island for detention.
The Chinese authorities confiscated all fishing tools, maritime equipment, 2,000 liters of oil, five diving cylinders, and a large amount of sea products.
Total value of the seized items of both fishing boats is estimated at VND900 million (US$43,200). Quan said.
At 12 am on May 21, the Chinese captors released all fishermen and the QNg 50003TS but kept the other boat in detention.
….but i have failed to find anything at all in the Chinese media about the incident.
Just two days later, precisely the opposite was the case. The May 19 edition of the Huanqiu Shibao ran an exclusive story headlined ‘Three foreign gunboats pursue and harass Chinese fishing boats, rescued by Yuzheng 310‘, which doesn’t appear to have been reported in the international media. It’s dramatic enough (and strange enough) to translate in full:
From Huanqiu Shibao‘s specially-dispatched journalist in the South China Sea: On May 18, China’s Yuzheng 310 vessel successfully deterred three gunboats from a certain country from pursuing and harassing 追袭 five Chinese fishing boats, protecting more than 100 Chinese fisherfolk from financial loss and personal harm.




“Hit’em”: APEC peacemaker Hu Jintao gets red carpet treatment from portal censors
Posted: September 7, 2012 | Author: Andrew Chubb | Filed under: China-Vietnam, Comment threads, PRC News Portals | Tags: APEC, censorship, Chinese internet, Chinese internet censorship, Chinese internet companies, CNS, 胡锦涛, Hu Jintao, manipulation of public opinion, online nationalism, phoenix, QQ, Sina, Sino-Vietnamese relations, south china sea, Tencent, Truong Tan Sang, uses of public opinion, Vladimir Putin, Vladivostok, Weibo, 南海, 中越 | 1 CommentTruong Tan Sang and Hu Jintao’s meeting at APEC 2012
Hu Jintao met with his Vietnamese counterpart yesterday at the APEC summit in Vladivostok, and made a rare official comment on the South China Sea disputes. From the China Daily’s report:
These cool-headed, restrained, joint-developing, dispute-shelving remarks were all over the PRC official media yesterday (Friday September 7), from when i first heard it on China National Radio, to the CNS report and the Foreign Ministry’s website.
The online mass media soon followed suit, with all the five top news portals except Netease having the story in their #1 or #2 headline slots by 12.25pm, and keeping them near the top until late in the evening.
Not surprisingly, given that “Hu Jintao” is a sensitive search term on the PRC internet, the comment threads were heavily censored. Phoenix’s has 25,000+ participants but only 92 comments (representing a KimLove Incredibility Ratio well above 250:1), the latest of which was posted at exactly 20.00 last night:
Being the last comment the website’s editors have decided to allow through, this earnest defence of Hu has stayed in place at the top of the page — but only those who choose to click the “newest comments” tab will see it.
By default, it’s the top comments, not the latest comments, that appear on readers’ screens, and they have to scroll a long way down through those, to the 14th comment to be precise, before they find anything remotely complimentary about Chairman Hu’s remarks — and even that appears to be posted by a foreigner.
Over at Sina, where as of 4am Saturday it remains the #3 story on the front page, the involvement of the censors is even more blatant: 1700-odd “participants” and only eight comments. In fact, that means i can translate the entire “conversation”. Here it is as it appears for readers (ie. from latest to earliest):
The pattern on the thread attached to the same story on Tencent’s news portal also appears to be the same as those on Phoenix and Sina: calls for war, sardonic criticism of Hu’s policy, and KIRs high enough to suggest most comments are being either deleted or hidden from view.
Given the importance of Chairmen Hu and Truong’s meeting, the high profile given to this story by all the PRC media, the fact that the story sat* prominently among the leading headlines on the portals, and the very obvious signs of rigging, it’s hard to see how the comments could represent anything other than exactly what the censors had decided the netizens should be seen to be saying.. The question in my mind is, who were the censors?
By default, of course, we must assume that the censors of news comment threads are always individual employees of PRC internet companies, in this case Sina and Phoenix. There’s presumably a management/command chain above them that leads up to some decision-making group within the company, though i have no idea of a.) how far above the “grass-roots” censors they are; b.) how far below the company’s top management they are; or c.) how they connect with the various relevant government bodies — e.g. MIIT, SCIO, Central & provincial Propaganda Depts.
It really seems a stretch to impute that the party or government would put out an instruction to major websites telling them to only allow comments calling for war with Vietnam on the day that the President calls for cooperation with Vietnam during a headline bilateral meeting at a major international forum.
Especially in CCP China, where the same president’s name cannot be searched on the country’s most vibrant social network.
Results for “Hu Jintao” not displayed due to relevant laws and regulations (02:17 September 8, 2o12)
—
* It continues to sit there even now at 4.50am the next day